Vitamin B for Dogs: Benefits, Side Effects, Foods & More
Tory JohnsonShare
Along with a healthy diet and plenty of exercise, vitamins play an important role in keeping your dog in great condition. But did you know that Vitamin B is one of the most important vitamins for dogs?
This complex vitamin is made up of eight different forms which can be found naturally in certain foods or added through a Vitamin B supplement.
It helps support cellular energy production, maintains skin and coat health, promotes digestion, supports nerve functions, and boosts immune system function.
Let's explore the benefits of Vitamin B for dogs as well as potential sources and deficiencies you should look out for.

What are B Vitamins
B Vitamins are a group of essential nutrients that play a crucial role in a dog's overall health and well-being. These vitamins are water soluble compounds, unlike the fat soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K.
Vitamin B deficiency can lead to a range of health problems such as anemia, skin disorders, and even neurological damage.
Fortunately, there are a variety of vitamin B supplements available that can help ensure your dog gets the proper nutrition they need.
The B complex vitamins, in particular, are essential for a healthy metabolism and can improve energy levels, boost the immune system, and even promote healthy skin and coat. Vitamin B complex includes all the essential B Vitamins - B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, and B12.
If you think your dog may be lacking in vitamin B, consult with your veterinarian to determine the best course of action and to run blood work if necessary.
Let's take an individual look at the B Vitamins.
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
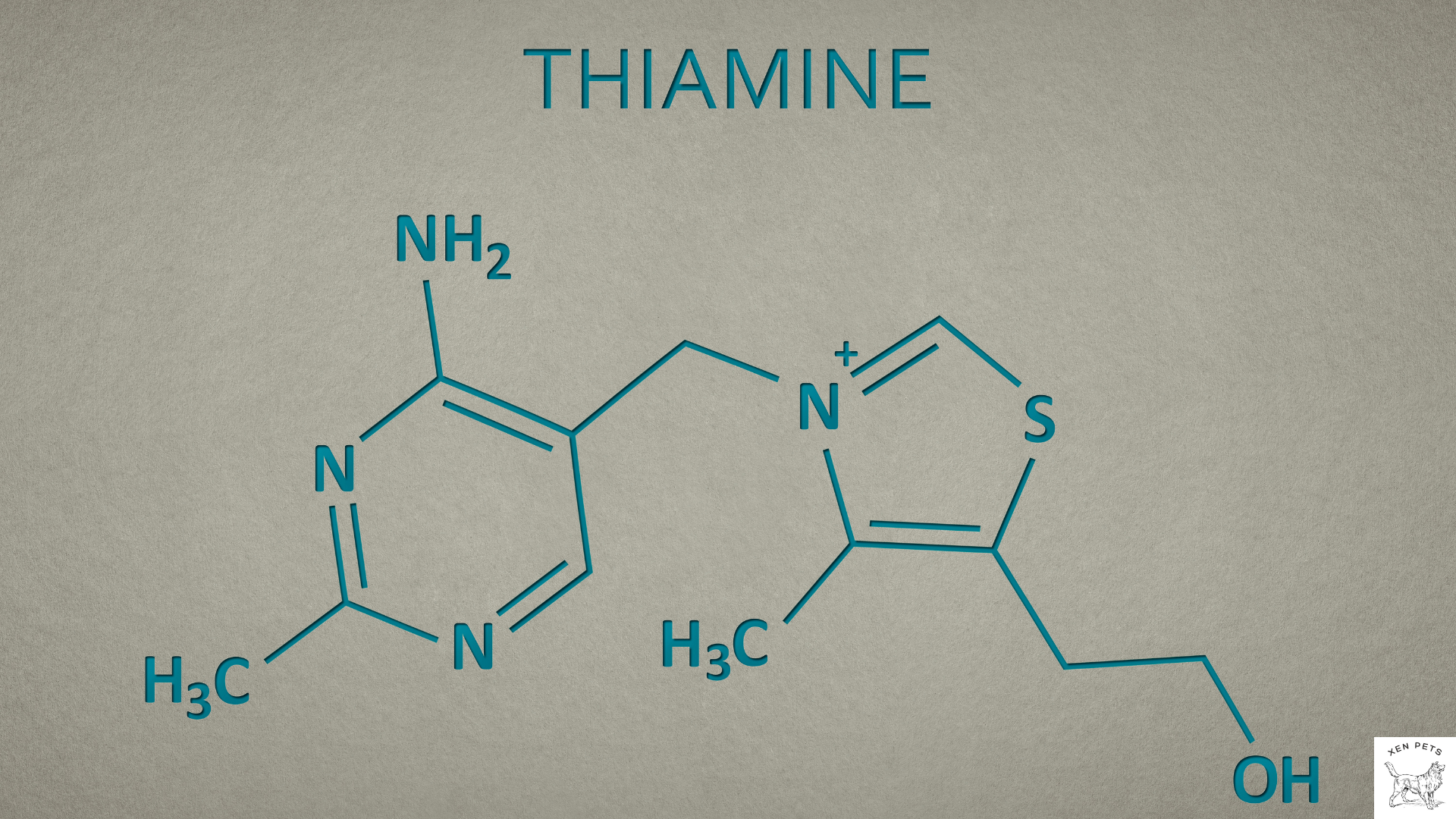
Thiamine for dogs is a critical vitamin for maintaining a healthy nervous system and energy production.
If your dog doesn't have enough thiamine in their diet or has a digestive issue preventing proper absorption, it can lead to a thiamine deficiency.
This can cause a range of problems such as loss of appetite, weakness, muscle atrophy, seizures, and even death in severe cases.
It’s important for dog owners to be aware of their pet’s thiamine levels and ensure they are receiving adequate intake through their food or supplements to maintain optimal health.
Thiamine food sources
- Fish
- Meat
- Poultry
- Some grains
- Eggs
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2, is an essential nutrient that plays a vital role in your dog's health.
It's responsible for helping to maintain healthy skin, coat, and eyesight, while also supporting a robust immune system and metabolism.
Riboflavin is water-soluble, meaning that it's not stored in the body, so it's important that dogs get enough of it in their diet regularly.
Without sufficient amounts of riboflavin, dogs may develop skin lesions, cataracts, anemia, and other health issues.
Riboflavin food sources
- Meat
- Eggs
- Dairy products
Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
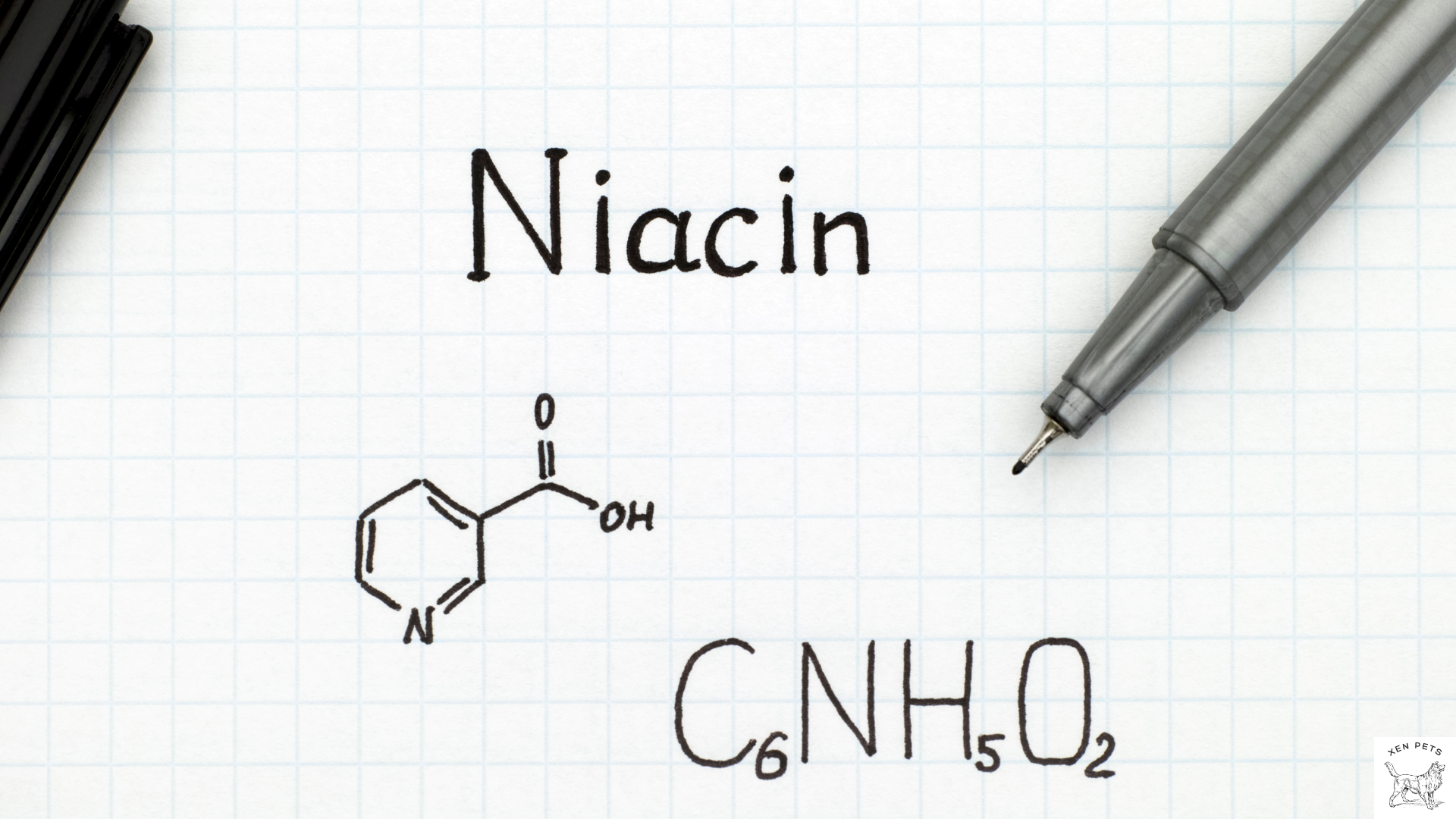
Niacin is another water-soluble nutrient. It aids in the metabolism of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates, which are essential for a healthy body.
Dogs, in particular, require niacin as it helps maintain their skin, coat, and nervous system health.
Additionally, niacin can enhance their joint mobility, reduce cholesterol levels, and promote healthy digestion.
However, dogs cannot produce niacin on their own, which means they need to obtain it from their diet or supplements.
It's crucial to note that excessive intake of niacin can also have adverse effects on a dog's health, making it imperative to consult with a veterinarian before adding supplements to their daily routine.
Dangers of niacin in dogs
Niacin side effects in dogs are uncommon but can include vomiting, diarrhea, and lack of appetite.
Niacin food sources
- Fish
- Poultry
- Organ meats (E.g. liver)
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid)

Pantothenic acid, also known as vitamin B5, is essential for both humans and dogs alike.
It plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including energy production, metabolism, and skin health.
In dogs, an adequate intake of pantothenic acid can help maintain healthy skin and a shiny coat, as well as support nerve transmission and adrenal function.
Pantothenic acid can also aid in the absorption of other nutrients, making it a vital nutrient for your furry friend's overall well-being.
While severe deficiencies are uncommon, it's always important to ensure that your dog's diet provides sufficient amounts of this crucial nutrient.
Pantothenic acid food sources
- Eggs
- Liver
- Brewer's yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae)
- Ginger root
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)
Pyridoxine, or Vitamin B6, plays an important role in ensuring the proper functioning of a dog's metabolism.
Pyridoxine can aid in the production of red blood cells, improve cognitive function, and support healthy skin and coat.
However, it's important to note that Pyridoxine cannot act alone in promoting optimal health for dogs. Other B Vitamins such as pantothenic acid help enhance the absorption and effectiveness of Pyridoxine.
Pyridoxine food sources
- Fish (Especially salmon, tuna, and cod)
- Organ meats (E.g. liver)
- Cooked sweet potatoes and white potatoes
Vitamin B7 (Biotin)
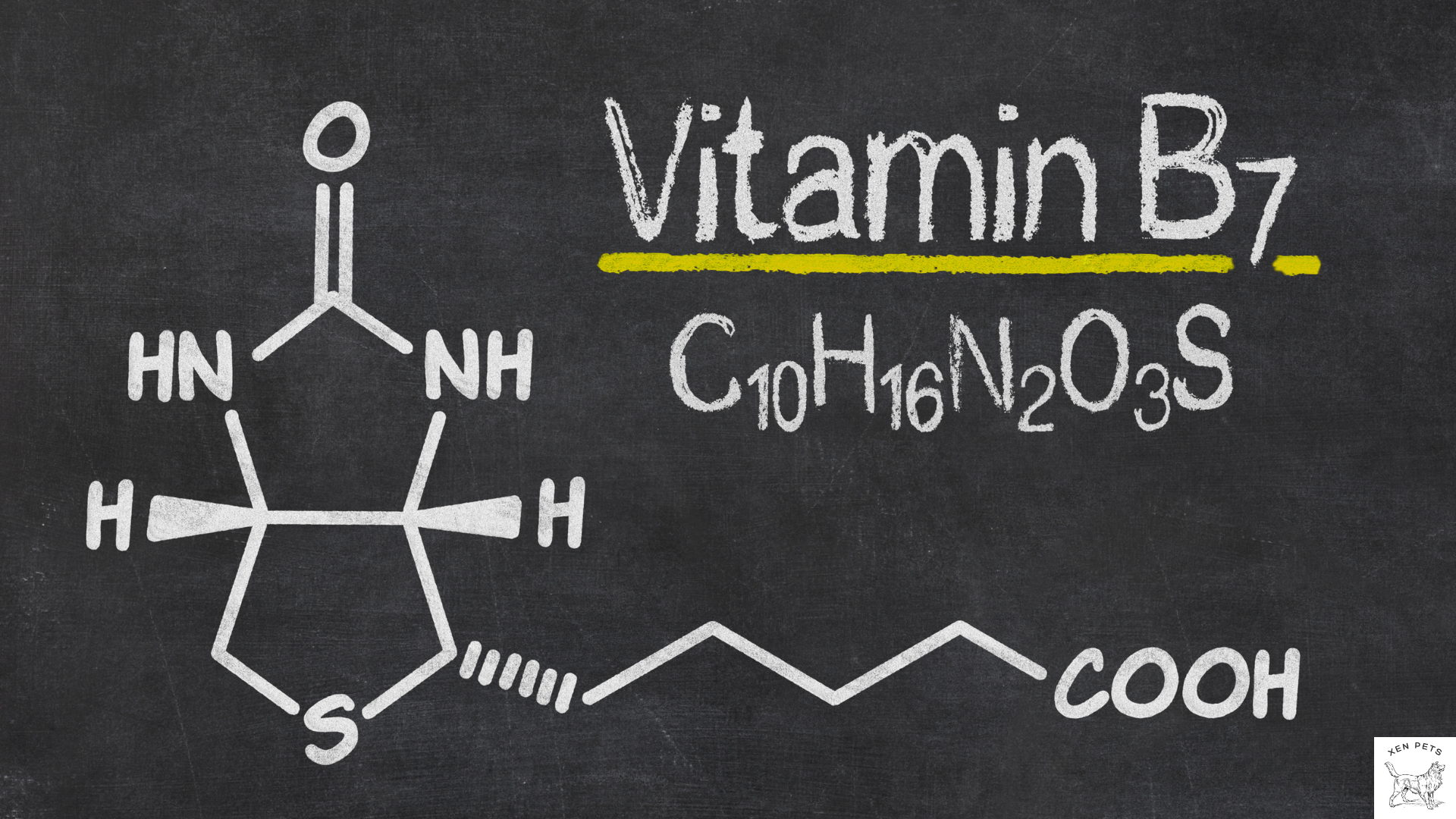
Biotin for dogs is a B-vitamin that is important for cell growth, metabolism, and healthy hair, skin, and nails.
Biotin deficiency can lead to skin problems, hair loss, and even neurological issues for dogs.
However, many high-quality dog foods already contain appropriate levels of biotin, so it is often not necessary to supplement a dog's diet with additional biotin unless a deficiency is diagnosed by a veterinarian.
Biotin food sources
- Dairy products
- Eggs
- Legumes
Vitamin B9 (Folate or folic acid)

Folate is a water-soluble nutrient that plays a crucial role in many of your dog's bodily functions.
It's essential for cell growth and maintenance, supports DNA synthesis, and helps red blood cells carry oxygen throughout the body.
Specifically for dogs, folate is necessary for metabolism, digestion, and cognitive function.
Without adequate levels of folate, dogs can experience anemia and other health issues.
Folate food sources
- Fruits (E.g. Apples and oranges)
- Cooked beans
- Green leafy vegetables (E.g. Lettuce, spinach, and cabbage)
Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)
For dogs, cobalamin is essential in promoting healthy nerve function, as well as aiding in the production of DNA and red blood cells. An inadequate amount of cobalamin in a dog's diet can lead to a range of health issues, including loss of appetite, weight loss, and lethargy.
Cobalamin food sources
- Fish
- Meat
- Poultry
- Dairy products
- Eggs
What is Vitamin B Complex for dogs?
Vitamin B complex for dogs is an all-inclusive blend of essential B vitamins. B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, and B12, are all important components of your dog's metabolic processes, acting as initiators of various cellular functions such as energy production, DNA synthesis, and nerve function.

Vitamin B Complex for dogs side effects
Vitamin B complex can provide numerous health benefits to dogs. However, as with any supplement or medication, there may be side effects to look out for.
One side effect worth noting is niacin toxicity, which can lead to vomiting, diarrhea, and a loss of appetite in dogs.
It's important to speak with a veterinarian before giving your dog any supplements, including those with Vitamin B complex, and to closely monitor their reactions to the supplement.
Bottom line
Taking care of your dog's health is incredibly important, and providing them with the right vitamins such as Vitamin B can be life changing to their overall wellbeing.
Check out our Nutrition Guides to learn more.